图论
- 判断树边,前向边,回边,横跨边
- 拓扑排序
- 二分图
- 二分图最大匹配
- 二分图最大权匹配: KM算法,复杂度O(n^3)
- 稳定婚姻问题,Gale-Shapley---婚姻匹配算法算法
- 网络流
- 最短路
- 差分约束与判负环
- 最小生成树
- 树
- 参考文献
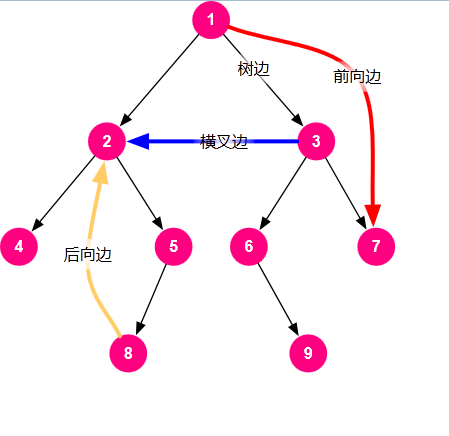
判断树边,前向边,回边,横跨边
- https://blog.csdn.net/u014665013/article/details/51351371
- https://blog.csdn.net/wshish920907/article/details/73276813
visited数组取值0, 1, 2
0, 尚未访问,表示树边。1,孩子还没访问完,表示回边。2,孩子访问完了,表示前向边/横跨边。
可以增加一个时间戳,记录每个节点首次访问的时间戳(访问dfs序)。当visited=2时,对于边 u -> v,若u的时间戳小于v的时间戳,则是前向边,否则是横跨边。
判断有没有环
即判断是否存在回边
https://leetcode.cn/problems/course-schedule/?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=graph
class Solution {
bool result = true;
void doDfs(
int &ts,
std::vector<int> &visited,
std::vector<int> &order,
std::vector<std::vector<int>> &graph,
int cur_node
) {
if (order[cur_node] > 0) {
return;
}
order[cur_node] = ts++;
visited[cur_node] = 1;
for (auto child : graph[cur_node]) {
if (visited[child] == 0) {
// tree edge
} else if (visited[child] == 1) {
// backward edge
result = false;
} else {
// cross edge or forward edge
if (order[cur_node] < order[child]) {
// forword edge
} else {
// cross edge
}
}
doDfs(ts, visited, order, graph, child);
}
visited[cur_node] = 2;
}
void dfs(std::vector<std::vector<int>> &graph) {
int ts = 1;
result = true;
std::vector<int> visited(graph.size(), 0), order(graph.size(), 0);
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); ++i) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
doDfs(ts, visited, order, graph, i);
}
}
}
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
for (auto &p : prerequisites) {
graph[p[1]].push_back(p[0]);
}
dfs(graph);
return result;
}
};
拓扑排序
节点带权重,在满足拓扑序的情况下,按权重高低优先输出。
思路:利用优先队列作为中间结构,每次将入度为0的点加入优先队列,然后取出最高优先级的点,并更新该点所有邻接点的入度,如果入度为0,则加入优先队列。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findOrder(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> graph(numCourses);
std::vector<int> in_degree(numCourses);
for (auto &e : prerequisites) {
graph[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
in_degree[e[0]]++;
}
std::queue<int> in_q;
for (int i = 0; i < in_degree.size(); ++i) {
if (in_degree[i] == 0) {
in_q.push(i);
}
}
std::vector<int> learn_order;
while (!in_q.empty()) {
auto node = in_q.front();
in_q.pop();
learn_order.push_back(node);
for (auto child : graph[node]) {
in_degree[child]--;
if (in_degree[child] == 0) {
in_q.push(child);
}
}
}
return learn_order.size() == numCourses ? learn_order : std::vector<int>();
}
};
二分图
性质
二分图不存在长度为奇数的环
因为每一条边都是从一个集合走到另一个集合,只有走偶数次才可能回到同一个集合。
判断一张图是不是二分图
dfs,如果存在奇环,则不是二分图;不存在奇环则是二分图
constexpr int MAX_N = 5001;
std::vector<int> graph[MAX_N];
int tag[MAX_N] = {0};
// example: is_bigraph(1, 1);
bool is_bigraph(int cur_v, int last_tag) {
tag[cur_v] = 3 - last_tag;
for (auto i : graph[cur_v]) {
if (tag[cur_v] == tag[i] || tag[i] == 0 && !is_bigraph(i, tag[cur_v])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
二分图最大匹配
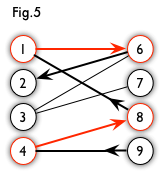
交替路:从一个未匹配点出发,依次经过非匹配边、匹配边、非匹配边…形成的路径叫交替路。
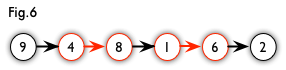
增广路:从一个未匹配点出发,走交替路,如果途径另一个未匹配点(出发的点不算),则这条交替路称为增广路(agumenting path)。例如,图 5 中的一条增广路如图 6 所示(图中的匹配点均用红色标出)
匈牙利算法:不停地找增广路,找到一条增广路,就把其中匹配边变非匹配,非匹配边变成匹配。1
DFS邻接矩阵版匈牙利算法(hdu2063)
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/7/15.
//
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
bool graph[501][501]; /* 邻接矩阵存有向图 u -> v */
bool matched[501]; /* 一次dfs中,v是否已经同一个u匹配 */
int link_u[501]; /* 点v同哪个u匹配 */
bool dfs(int u, int v_num) {
for (int v = 1; v <= v_num; ++v) {
if (graph[u][v] && !matched[v]) {
matched[v] = true;
if (link_u[v] == -1 || dfs(link_u[v], v_num)) {
link_u[v] = u;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 匈牙利算法求二分图最大匹配。(左右两边点的编号均从1开始)
* @param u_num 左边一组点的个数
* @param v_num 右边一组点的个数
* @return 最大匹配数
*/
int hungary(int u_num, int v_num) {
int result = 0;
memset(link_u, -1, sizeof(link_u));
for (int i = 1; i <= u_num; ++i) {
memset(matched, false, sizeof(matched));
if (dfs(i, v_num)) ++result;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
int k, m, n;
while (scanf("%d", &k) && k) {
scanf("%d %d", &m, &n);
memset(graph, false, sizeof(graph));
int u, v;
while (k--) {
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
graph[u][v] = true;
}
printf("%d\n", hungary(m, n));
}
return 0;
}
二分图最大权匹配: KM算法,复杂度O(n^3)
考虑到二分图中两个集合中的点并不总是相同,为了能应用 KM 算法解决二分图的最大权匹配,需要先作如下处理:将两个集合中点数比较少的补点,使得两边点数相同,再将不存在的边权重设为 0,这种情况下,问题就转换成求 最大权完美匹配问题 ,从而能应用 KM 算法求解。
给定一张二分图,左右部均有 n 个点,共有 m 条带权边,且保证有完美匹配。
求一种完美匹配的方案,使得最终匹配边的边权之和最大。
输出第一行表示答案。第二行共 n 个整数 $$a_1,a_2,a_3\cdots a_n$$,其中 $$a_i$$表示完美匹配下与右部第 i 个点相匹配的左部点的编号。
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/9/28.
//
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
class KM {
#define MAX_N 605
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
public:
static long long graph[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 边权邻接矩阵
private:
static long long lx[MAX_N], ly[MAX_N], slack[MAX_N], pre[MAX_N];
static int linker[MAX_N]; // linker[i]:与右边第i个点相匹配的左边的点
static bool vis_y[MAX_N]; // 标记右边点集是否被访问过
static void bfs(int k, int n);
public:
static long long solve(int n);
static void print_linker(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; ++i) {
printf("%d ", KM::linker[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", KM::linker[n]);
}
};
long long KM::graph[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 边权邻接矩阵
long long KM::lx[MAX_N], KM::ly[MAX_N], KM::slack[MAX_N], KM::pre[MAX_N];
bool KM::vis_y[MAX_N];
int KM::linker[MAX_N];
void KM::bfs(int k, int n) {
long long x, y = 0, yy = 0, delta;
memset(pre, 0, sizeof(pre));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) slack[i] = INF;
linker[y] = k;
while (true) {
x = linker[y];
delta = INF;
vis_y[y] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis_y[i]) {
if (slack[i] > lx[x] + ly[i] - graph[x][i]) {
slack[i] = lx[x] + ly[i] - graph[x][i];
pre[i] = y;
}
if (slack[i] < delta) delta = slack[i], yy = i;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (vis_y[i]) lx[linker[i]] -= delta, ly[i] += delta;
else slack[i] -= delta;
}
y = yy;
if (linker[y] == -1) break;
}
while (y) linker[y] = linker[pre[y]], y = pre[y];
}
long long KM::solve(int n) {
memset(lx, 0, sizeof(lx));
memset(ly, 0, sizeof(ly));
memset(linker, -1, sizeof(linker));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
memset(vis_y, false, sizeof(vis_y));
bfs(i, n);
}
long long res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (linker[i] != -1) {
res += graph[linker[i]][i];
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
int n;
static long long m, x, y, weight;
scanf("%lld %lld", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
KM::graph[i][j] = -INF;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%lld %lld %lld", &x, &y, &weight);
KM::graph[x][y] = weight;
}
printf("%lld\n", KM::solve(n));
KM::print_linker(n);
return 0;
}
2019南京区域赛spy
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
class KM {
#define MAX_N 605
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
public:
static long long graph[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 边权邻接矩阵
private:
static long long lx[MAX_N], ly[MAX_N], linker[MAX_N], slack[MAX_N], pre[MAX_N];
static bool vis_y[MAX_N]; // 标记右边点集是否被访问过
static void bfs(long long k, int n);
public:
static long long solve(int n);
};
long long KM::graph[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 边权邻接矩阵
long long KM::lx[MAX_N], KM::ly[MAX_N], KM::linker[MAX_N], KM::slack[MAX_N], KM::pre[MAX_N];
bool KM::vis_y[MAX_N];
void KM::bfs(long long k, int n) {
long long x, y = 0, yy = 0, delta;
memset(pre, 0, sizeof(pre));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) slack[i] = INF;
linker[y] = k;
while (true) {
x = linker[y];
delta = INF;
vis_y[y] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis_y[i]) {
if (slack[i] > lx[x] + ly[i] - graph[x][i]) {
slack[i] = lx[x] + ly[i] - graph[x][i];
pre[i] = y;
}
if (slack[i] < delta) delta = slack[i], yy = i;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (vis_y[i]) lx[linker[i]] -= delta, ly[i] += delta;
else slack[i] -= delta;
}
y = yy;
if (linker[y] == -1) break;
}
while (y) linker[y] = linker[pre[y]], y = pre[y];
}
long long KM::solve(int n) {
memset(lx, 0, sizeof(lx));
memset(ly, 0, sizeof(ly));
memset(linker, -1, sizeof(linker));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
memset(vis_y, false, sizeof(vis_y));
bfs(i, n);
}
long long res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (linker[i] != -1) {
res += graph[linker[i]][i];
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
static long long a[MAX_N], b[MAX_N], c[MAX_N], p[MAX_N];
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%lld", &p[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%lld", &b[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%lld", &c[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
long long s = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
if (b[i] + c[j] > a[k]) s += p[k];
}
KM::graph[i][j] = s;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", KM::solve(n));
return 0;
}
稳定婚姻问题,Gale-Shapley---婚姻匹配算法算法
图论算法:稳定婚姻问题,如何找到最适合自己的另一半 - 博文视点Broadview的文章 - 知乎
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/436991506
https://blog.csdn.net/Air_hjj/article/details/70828937
网络流
最大流
Dinic
时间复杂度:$$O(n^2m)$$
BFS构造分层图。DFS根据分层往下遍历,回溯时更新边权。
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX_V_NUM 200
#define MAX_E_NUM 5000
const int INF = 0x3fffffff;
int edge_idx = 1, start_head[MAX_V_NUM + 4];
/* 2、3是一对反向边;4、5是一对反向边... */
struct Edge {
int to, next, remain_capacity;
static int head[MAX_V_NUM + 4];
} edges[MAX_E_NUM * 2 + 4];
int Edge::head[MAX_V_NUM + 4] = {0};
int depth[MAX_V_NUM + 4];
/**
* 添加双向边
* @param u 起点
* @param v 终点
* @param w 边权
*/
static void add_edges(int u, int v, int w) {
edges[++edge_idx] = {v, Edge::head[u], w};
Edge::head[u] = edge_idx;
edges[++edge_idx] = {u, Edge::head[v], 0};
Edge::head[v] = edge_idx;
}
/* 在残量网络中构造分层图 */
bool bfs(int source, int n, int target) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) depth[i] = INF;
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(source);
depth[source] = 0;
start_head[source] = Edge::head[source];
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = Edge::head[x]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
int v = edges[i].to;
if (edges[i].remain_capacity > 0 && depth[v] == INF) {
q.push(v);
start_head[v] = Edge::head[v];
depth[v] = depth[x] + 1;
if (v == target) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 只对下一层级的点进行dfs
* @param cur_v 当前所在的点
* @param cur_min_flow 增广路上最小的边权(剩余容量)
* @return 经过cur_v流出的总容量
*/
int dfs(int cur_v, int cur_min_flow, const int target) {
if (cur_v == target) return cur_min_flow;
// min_flow是当前最小的剩余容量
int min_flow, result = 0;
for (int i = start_head[cur_v]; i && cur_min_flow > 0; i = edges[i].next) {
// 当前弧优化
start_head[cur_v] = i;
int next_v = edges[i].to;
if (edges[i].remain_capacity > 0 && (depth[next_v] == depth[cur_v] + 1)) {
min_flow = dfs(next_v, std::min(cur_min_flow, edges[i].remain_capacity), target);
// 剪枝,去掉增广完毕的点
if (min_flow == 0) depth[next_v] = INF;
edges[i].remain_capacity -= min_flow;
edges[i ^ 1].remain_capacity += min_flow;
result += min_flow;
cur_min_flow -= min_flow;
}
}
return result;
}
int main() {
int n, m, source, target;
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n, &m, &source, &target);
int u, v, w;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &w);
add_edges(u, v, w);
}
long long ans = 0;
while (bfs(source, n, target)) {
ans += dfs(source, INF, target);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
最短路
Dijkstra
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/3/8.
// hdu2544
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
const long long MAX_LONG_LONG = 9223372036854775807;
struct Edge {
static int edge_idx;
static int heads[100005];
int to;
long long distance;
int next;
bool operator<(Edge &e) const {
return distance < e.distance;
}
} edges[200005];
int Edge::edge_idx = 0;
int Edge::heads[100005] = {0};
struct Vertex {
int v;
long long distance;
Vertex(int v, long long distance) : v(v), distance(distance) {}
bool operator<(const Vertex &vertex) const {
return distance > vertex.distance;
}
};
void add_edge(int from, int to, long long distance) {
edges[++Edge::edge_idx] = {to, distance, Edge::heads[from]};
Edge::heads[from] = Edge::edge_idx;
}
long long distance[100005];
bool visited[100005];
void dijkstra(int vertex_count) {
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
distance[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= vertex_count; ++i) {
distance[i] = MAX_LONG_LONG;
}
std::priority_queue<Vertex> vertex_queue;
// 1是起点
vertex_queue.push({1, 0});
while (!vertex_queue.empty()) {
Vertex cur_v = vertex_queue.top();
vertex_queue.pop();
if (visited[cur_v.v]) continue;
// 搜索到终点结束
if (cur_v.v == vertex_count) break;
visited[cur_v.v] = true;
for (int i = Edge::heads[cur_v.v]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
if (!visited[edges[i].to] && distance[edges[i].to] > distance[cur_v.v] + edges[i].distance) {
distance[edges[i].to] = distance[cur_v.v] + edges[i].distance;
vertex_queue.push({edges[i].to, distance[edges[i].to]});
}
}
}
printf("%lld\n", distance[vertex_count]);
}
int main() {
int vertex_count, road_count;
int from, to, tmp_dis;
while (~scanf("%d %d", &vertex_count, &road_count) && vertex_count && road_count) {
Edge::edge_idx = 0;
memset(Edge::heads, 0, sizeof(Edge::heads));
for (int i = 0; i < road_count; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &from, &to, &tmp_dis);
add_edge(from, to, tmp_dis);
add_edge(to, from, tmp_dis);
}
dijkstra(vertex_count);
}
return 0;
}
Floyd
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/7/18.
// hdu2544
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int graph[100][100];
void floyd(int n) {
for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
graph[i][j] = std::min(graph[i][j], graph[i][k] + graph[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
while (~scanf("%d %d", &n, &m) && n && m) {
int u, v, w;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
graph[i][j] = INF;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &w);
graph[u][v] = graph[v][u] = w;
}
floyd(n);
printf("%d\n", graph[1][n]);
}
return 0;
}
SPFA
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/7/19.
// luogu3371
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define MAX_V_NUM 10000
#define MAX_EDGE_NUM 500000
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
struct Edge {
int to, next, weight;
static int idx;
static int head[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
} edges[MAX_EDGE_NUM + 2];
int Edge::idx = 0;
int Edge::head[MAX_V_NUM + 2] = {0};
inline void add_edge(int u, int v, int weight) {
edges[++Edge::idx] = {v, Edge::head[u], weight};
Edge::head[u] = Edge::idx;
}
int distance[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
void spfa(int n, int start_v) {
static bool in_queue[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
distance[i] = INF;
in_queue[i] = false;
}
std::queue<int> v_queue;
v_queue.push(start_v);
in_queue[start_v] = true;
distance[start_v] = 0;
while (!v_queue.empty()) {
int cur_v = v_queue.front();
v_queue.pop();
in_queue[cur_v] = false;
for (int i = Edge::head[cur_v]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
int to = edges[i].to;
if (distance[cur_v] + edges[i].weight < distance[to]) {
distance[to] = distance[cur_v] + edges[i].weight;
if (!in_queue[to]) {
v_queue.push(to);
in_queue[to] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, m, start;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &start);
int u, v, weight;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &weight);
add_edge(u, v, weight);
}
spfa(n, start);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
printf("%d%c", distance[i], (i != n ? ' ' : '\n'));
}
return 0;
}
差分约束与判负环
差分约束系统 是一种特殊的$$n$$元一次不等式组,它包含$$n$$个变量$$x_1,x_2,...,x_n$$以及$$m$$个约束条件,每个约束条件是由两个其中的变量做差构成的,形如 $$x_i - x_j \le c_k$$,其中$$c_k$$ 是常数(可以是任意整数)。我们要解决的问题是:求一组解$$x_1=a_1, x_2=a_2,...,x_n = a_n$$ ,使得所有的约束条件得到满足,否则判断出无解。
差分约束系统中的每个约束条件 $$x_i - x_j \le c_k$$ 都可以变形成 $$x_i \le x_j + c_k$$ ,这与单源最短路中的三角形不等式$$dist[y] \le dist[x] + z$$ 非常相似。因此,我们可以把每个变量$$x_i$$ 看做图中的一个结点,对于每个约束条件$$x_i - x_j \le c_k$$ ,从结点$$j$$ 向结点$$i$$ 连一条长度为 $$c_k$$的有向边。
注意到,如果$${a_1, a_2, ...,a_n}$$ 是该差分约束系统的一组解,那么对于任意的常数$$d$$ ,$${a_1 + d, a_2 + d, ...,a_n + d}$$ 显然也是该差分约束系统的一组解,因为这样做差后$$d$$ 刚好被消掉。
设$$dist[0] = 0$$ 并向每一个点连一条边,跑单源最短路,若图中存在负环,则给定的差分约束系统无解,否则,$$x_i = dist[i]$$ 为该差分约束系统的一组解。
一般使用 Bellman-Ford 或队列优化的 Bellman-Ford(俗称 SPFA,在某些随机图跑得很快)判断图中是否存在负环,最坏时间复杂度为$$O(nm)$$ 。
| 题意 | 转换 | 加边 |
|---|---|---|
| $$x_a - x_b \ge c$$ | $$x_b - x_a \le -c$$ | add_edge(a, b, -c) |
| $$x_a - x_b \le c$$ | $$x_a - x_b \le c$$ | add_edge(b, a, c) |
| $$x_a = x_b$$ | $$x_a - x_b \le 0, \space x_b - x_a \le 0$$ | add_edge(b, a, 0) add_edge(a, b, 0) |
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/7/19.
// luogu 1993
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define MAX_V_NUM 10000
#define MAX_EDGE_NUM 500000
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
struct Edge {
int to, next, weight;
static int idx;
static int head[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
} edges[MAX_EDGE_NUM + 2];
int Edge::idx = 0;
int Edge::head[MAX_V_NUM + 2] = {0};
inline void add_edge(int u, int v, int weight) {
edges[++Edge::idx] = {v, Edge::head[u], weight};
Edge::head[u] = Edge::idx;
}
int distance[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
/**
* 判断是否有负环
* @param n 图中点的个数
* @param start_v 起点
* @return 有负环: true; 没有: false
*/
bool spfa(int n, int start_v) {
static bool in_queue[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
static int count[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
distance[i] = INF;
in_queue[i] = false;
count[i] = 0;
}
std::queue<int> v_queue;
v_queue.push(start_v);
in_queue[start_v] = true;
distance[start_v] = 0;
while (!v_queue.empty()) {
int cur_v = v_queue.front();
v_queue.pop();
in_queue[cur_v] = false;
for (int i = Edge::head[cur_v]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
int to = edges[i].to;
if (distance[cur_v] + edges[i].weight < distance[to]) {
distance[to] = distance[cur_v] + edges[i].weight;
if (++count[to] >= n) return true;
if (!in_queue[to]) {
v_queue.push(to);
in_queue[to] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
int op, u, v, c;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &c);
add_edge(u, v, -c);
} else if (op == 2) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &c);
add_edge(v, u, c);
} else {
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
add_edge(u, v, 0);
add_edge(v, u, 0);
}
}
// 保证图是连通的
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
add_edge(n + 1, i, 0);
puts(spfa(n + 1, n + 1) ? "No" : "Yes");
return 0;
}
SPFA判负环
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/7/19.
// luogu p3385
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define MAX_V_NUM 2003
#define MAX_EDGE_NUM 6003
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
struct Edge {
int to, next, weight;
static int idx;
static int head[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
} edges[MAX_EDGE_NUM + 2];
int Edge::idx = 0;
int Edge::head[MAX_V_NUM + 2] = {0};
inline void add_edge(int u, int v, int weight) {
edges[++Edge::idx] = {v, Edge::head[u], weight};
Edge::head[u] = Edge::idx;
}
int distance[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
/**
* 判断是否有负环
* @param n 图中点的个数
* @param start_v 起点
* @return 有负环: true; 没有: false
*/
bool spfa(int n, int start_v) {
static bool in_queue[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
static int count[MAX_V_NUM + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
distance[i] = INF;
in_queue[i] = false;
count[i] = 0;
}
std::queue<int> v_queue;
v_queue.push(start_v);
in_queue[start_v] = true;
distance[start_v] = 0;
while (!v_queue.empty()) {
int cur_v = v_queue.front();
v_queue.pop();
in_queue[cur_v] = false;
for (int i = Edge::head[cur_v]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
int to = edges[i].to;
if (distance[cur_v] + edges[i].weight < distance[to]) {
distance[to] = distance[cur_v] + edges[i].weight;
if (++count[to] >= n) return true;
if (!in_queue[to]) {
v_queue.push(to);
in_queue[to] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
Edge::idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) Edge::head[i] = 0;
int u, v, w;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &w);
add_edge(u, v, w);
if (w >= 0) {
add_edge(v, u, w);
}
}
puts(spfa(n, 1) ? "YES" : "NO");
}
return 0;
}
最小生成树
Prim在稠密图中比Kruskal优,在稀疏图中比Kruskal劣
Prim
O(E + VlgV)
//
// Created by Jiang Yinzuo on 2020/7/18.
// luogu p3366
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#define MAX_V_NUM 5000
#define MAX_E_NUM 200000
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
struct Edge {
int to, next, weight;
static int idx;
static int head[MAX_V_NUM + 1];
bool operator<(const Edge &e) const {
return this->weight < e.weight;
}
} edges[MAX_E_NUM * 2 + 1];
int Edge::idx = 0;
int Edge::head[MAX_V_NUM + 1] = {0};
static inline void add_edge(int u, int v, int weight) {
edges[++Edge::idx] = {v, Edge::head[u], weight};
Edge::head[u] = Edge::idx;
}
/**
* prim算法求最小生成树
* @param n 图中点的个数
* @return 最小生成树的权值之和。返回-1表示图不连通
*/
int prim(int n) {
static bool added_v[MAX_V_NUM + 1];
static int min_weight[MAX_V_NUM + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) min_weight[i] = INF;
memset(added_v, false, sizeof(added_v));
int added_v_num = 1;
int cur_v = 1;
int result = 0;
added_v[cur_v] = true;
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>, std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>, std::greater<> > queue;
for (int i = Edge::head[cur_v]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
queue.push({edges[i].weight, edges[i].to});
}
while (!queue.empty() && added_v_num < n) {
auto edge = queue.top();
queue.pop();
if (added_v[edge.second]) continue;
added_v[edge.second] = true;
result += edge.first;
added_v_num++;
for (int i = Edge::head[edge.second]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
if (!added_v[edges[i].to] && edges[i].weight < min_weight[edges[i].to]) {
min_weight[edges[i].to] = edges[i].weight;
queue.push({edges[i].weight, edges[i].to});
}
}
}
if (added_v_num < n) return -1;
return result;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
int u, v, w;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &w);
add_edge(u, v, w);
add_edge(v, u, w);
}
int result = prim(n);
if (result >= 0) printf("%d\n", result);
else {
printf("orz\n");
}
return 0;
}
O(ElgV)
树
图判树
方法一: 图连通且边数等于点数减一就是树。
方法二: 从任意一点开始DFS,如果DFS过程中有环,那么不是树。同时整个图必须是连通的。
LCA
倍增求LCA
/**
* luogu3379
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int v;
int next;
} edges[500002 << 1];
int heads[500002];
int total = 0;
int depth[500002] = {0};
int ancestors[500002][22] = {0};
int LOG_2[500002];
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
edges[++total] = {v, heads[u]};
heads[u] = total;
}
void dfs(int cur_v, int parent) {
ancestors[cur_v][0] = parent;
depth[cur_v] = depth[parent] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= LOG_2[depth[cur_v]]; ++i) {
ancestors[cur_v][i] = ancestors[ancestors[cur_v][i-1]][i-1];
}
for (int i = heads[cur_v]; i; i = edges[i].next) {
if (edges[i].v != parent) {
dfs(edges[i].v, cur_v);
}
}
}
int lca(int a, int b) {
if (depth[a] < depth[b]) {
swap(a, b);
}
while (depth[a] > depth[b]) {
a = ancestors[a][LOG_2[depth[a]-depth[b]]];
}
if (a == b) {
return a;
}
for (int i = LOG_2[depth[a]]; i >= 0; --i) {
if (ancestors[a][i] != ancestors[b][i]) {
a = ancestors[a][i];
b = ancestors[b][i];
}
}
return ancestors[a][0];
}
void get_log_2() {
LOG_2[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= 500001; ++i) {
LOG_2[i] = LOG_2[i>>1] + 1;
}
}
int main() {
get_log_2();
int n, m, s;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &s);
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
add_edge(x, y);
add_edge(y, x);
}
dfs(s, 0);
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
printf("%d\n", lca(a, b));
}
return 0;
}
树的直径
解法
两次dfs/bfs
先从任意一点P出发,找离它最远的点Q,再从点Q出发,找离它最远的点W,W到Q的距离就是是的直径
树形DP
树的中心
树的中心: 所有节点中,到树中其他节点的最远距离 最小的节点。树的中心有1个或2个。
[leetcode例题](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees)
```c++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> graph(n);
for (auto &e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
std::vector<int> parents(n, -1);
int x = bfs(graph, parents, 0);
int y = bfs(graph, parents, x);
std::vector<int> path;
while (y != -1) {
path.push_back(y);
y = parents[y];
}
return path.size() % 2 == 1 ? std::vector({path[path.size() / 2]}) : std::vector({path[path.size() / 2 - 1], path[path.size() / 2]});
}
int bfs(const std::vector<std::vector<int>> &graph,
std::vector<int> &parents,
int cur_node) {
parents[cur_node] = -1;
std::vector<bool> visited(graph.size(), false);
visited[cur_node] = true;
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(cur_node);
while (!q.empty()) {
cur_node = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto child : graph[cur_node]) {
if (!visited[child]) {
parents[child] = cur_node;
q.push(child);
visited[child] = true;
}
}
}
return cur_node;
}
};